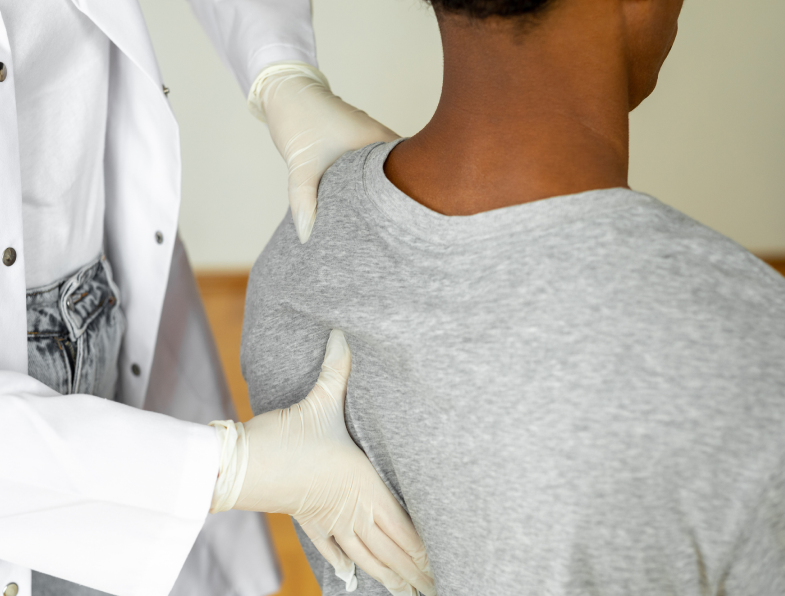
What is a Herniated Disc?
A herniated disc, also known as a slipped or ruptured disc, is a common spinal condition that occurs when the soft, gel-like center of an intervertebral disc pushes through a crack in the tougher exterior casing. This condition most frequently affects the lower back (lumbar spine) but can also occur in the neck (cervical spine).
The spinal column consists of a series of bones (vertebrae) stacked on top of one another. Between each vertebra are flexible intervertebral discs that act as cushions, absorbing shock and allowing for spinal flexibility. Each disc has a tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and a soft inner core (nucleus pulposus).
When a disc herniates, the inner core pushes out through a tear in the outer layer. This can irritate nearby nerves, leading to pain, numbness, or weakness in an arm or leg, depending on the location of the herniated disc.